 Long, course hairs that make up the cat's top coat. These carry the pattern of the fur.... ↪ Read more
Long, course hairs that make up the cat's top coat. These carry the pattern of the fur.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
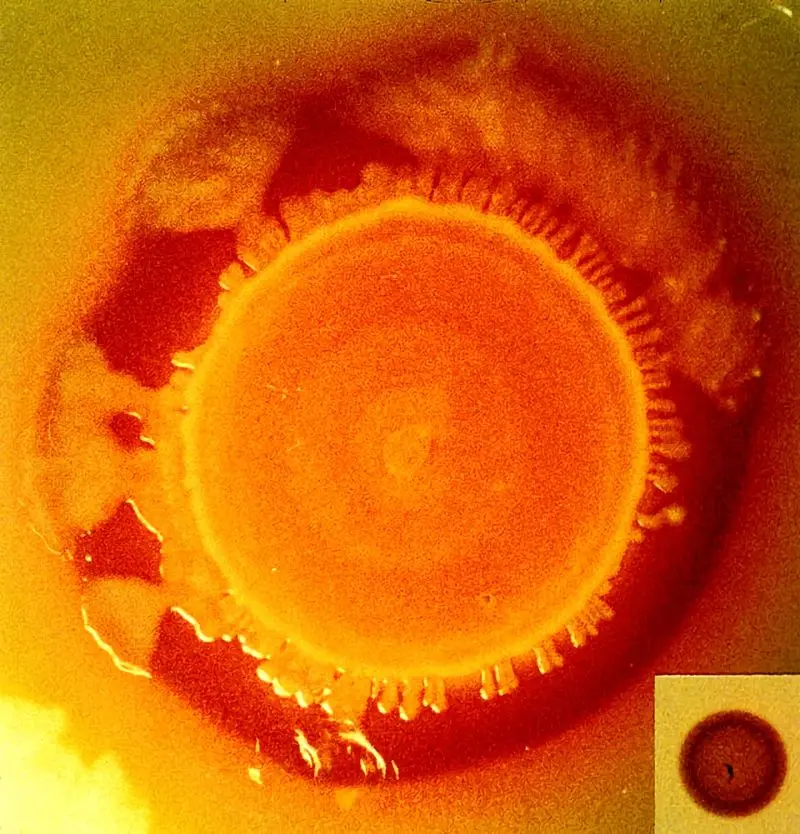 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
Guard Hair
 Long, course hairs that make up the cat's top coat. These carry the pattern of the fur.... ↪ Read more
Long, course hairs that make up the cat's top coat. These carry the pattern of the fur.... ↪ Read more Grooming Kit
 A collection of materials needed for the care of a cat's coat, including brush, comb and feline shampoo.... ↪ Read more
A collection of materials needed for the care of a cat's coat, including brush, comb and feline shampoo.... ↪ Read more Genus
 A biological classification that combines organisms sharing common characteristics; ranks between species and family.... ↪ Read more
A biological classification that combines organisms sharing common characteristics; ranks between species and family.... ↪ Read more Genetic
Free-feed
Flehmening
Fleas
Feral Cat
Feline Leukaemia
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
 A virus that invades the cat's DNA and uses it to reproduce, causing dysfunction of the immune system.... ↪ Read more
A virus that invades the cat's DNA and uses it to reproduce, causing dysfunction of the immune system.... ↪ Read more Feline
Fat
 A concentrated food source of oily, water-insoluble glyceride compounds that combine oxygen, hydrogen and carbon. A term used in a general sense to refer to both fats and oils. Fat supplied 2. 25 times as much energy as carbohydrates. Both fats and oils share the same general structure and chemical... ↪ Read more
A concentrated food source of oily, water-insoluble glyceride compounds that combine oxygen, hydrogen and carbon. A term used in a general sense to refer to both fats and oils. Fat supplied 2. 25 times as much energy as carbohydrates. Both fats and oils share the same general structure and chemical... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Echocardiogram Ectoparasite Ectopic Edema Electrocardiogram (EKG) Electrolyte Emesis EncephalopathyPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Wexler Animal Hospital, 458-D Heymann Boulevard Lafayette, LA 70503 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA PenBay Veterinary Associates, 599 Commercial Street, Rockport Penobscot Veterinary Services, 411 Davis Road Bangor, ME USA Pine Tree Veterinary Hospital, 220 Western Avenue Augusta, ME 04330 USA River Road Veterinary Hospital, 210 River Road Orrington, ME 04474 USA Scarborough Animal Hospital, 29 First Street, Scarborough, ME Veterinary & Rehabilitation Center Of Cape Elizabeth, 207 Ocean House Road Cape Elizabeth, ME 04107 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
SULFASALAZINE Doses - SULFASALAZINE TERBUTALINE SULFATE Doses - TERBUTALINE SULFATE TESTOSTERONE CYPIONATE, TESTOSTERONE ENANTHATE, TESTOSTERONE PROPRIONATE Doses - TESTOSTERONE CYPIONATE, TESTOSTERONE ENANTHATE, TESTOSTERONE PROPRIONATE TETRACYCLINE HCL Doses - TETRACYCLINE HCLPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Light feeder Limbic Limited feeding Linea alba Lineal gland Lingual surface Histopathologic Hivesveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2025 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online








