 An oral medication that can be used to control blood glucose levels in some diabetic cats who still have some insulin production.... ↪ Read more
An oral medication that can be used to control blood glucose levels in some diabetic cats who still have some insulin production.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
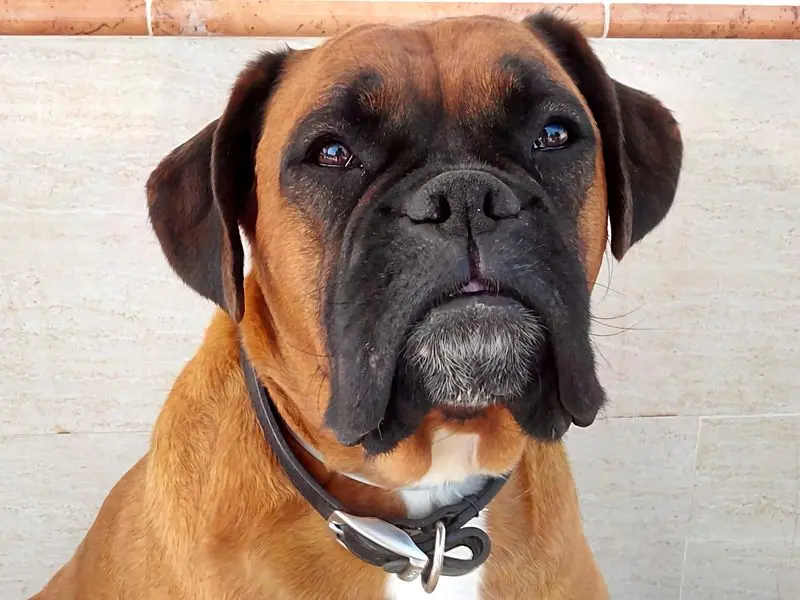 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
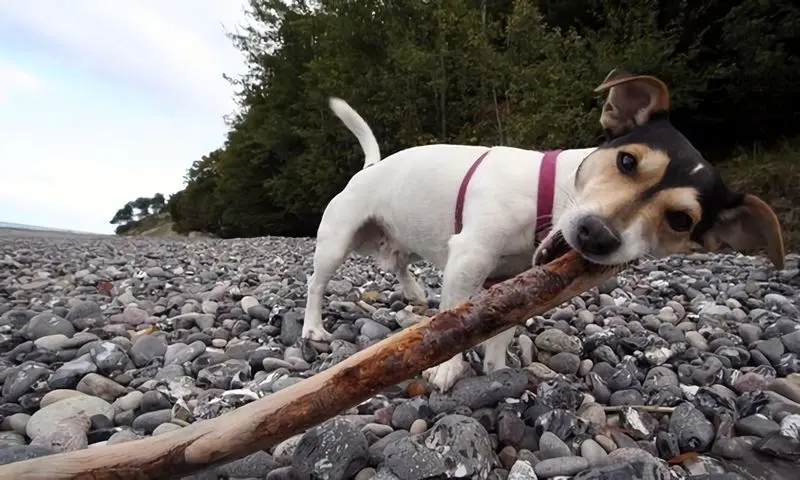 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
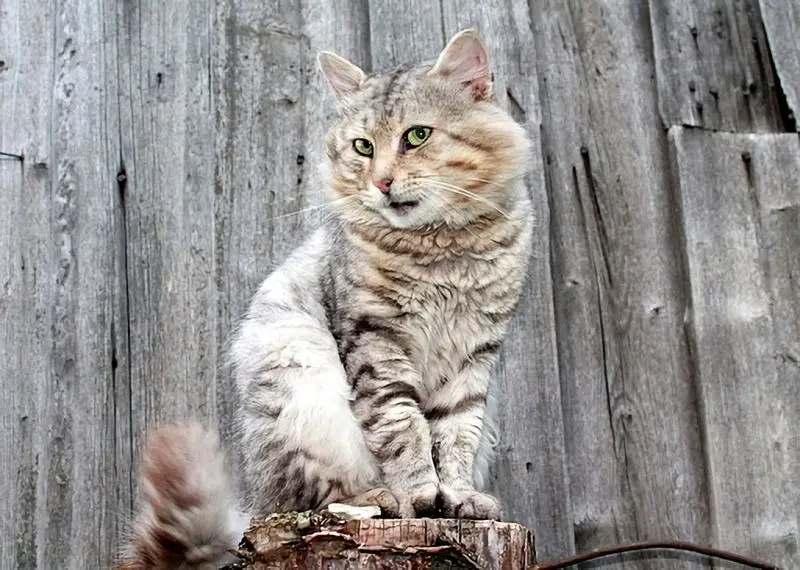 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
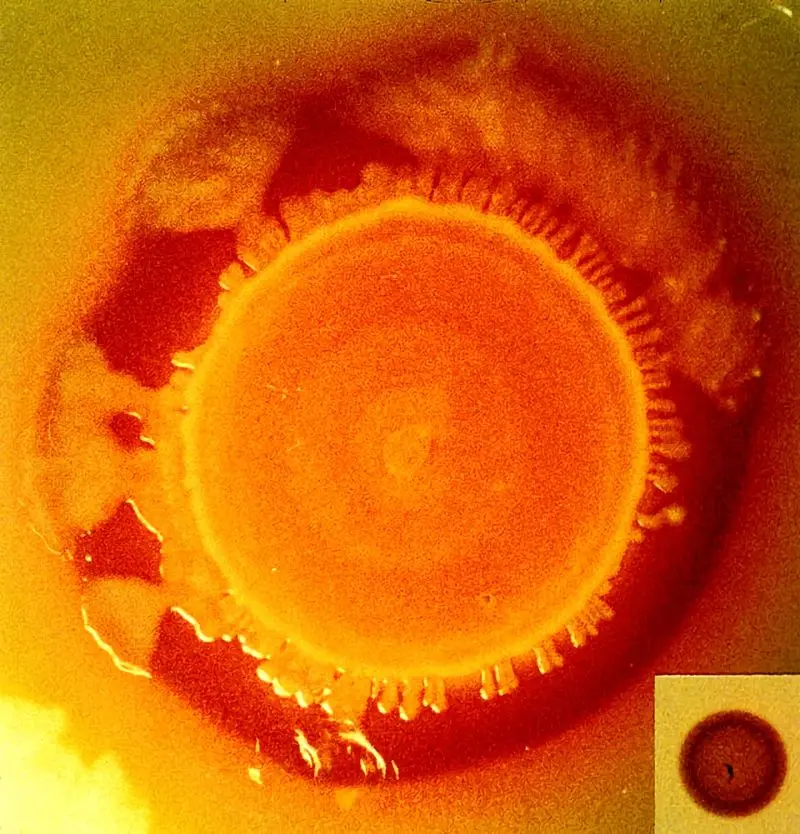 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
Glipizide
 An oral medication that can be used to control blood glucose levels in some diabetic cats who still have some insulin production.... ↪ Read more
An oral medication that can be used to control blood glucose levels in some diabetic cats who still have some insulin production.... ↪ Read more Gingival
Gestation
Gastrointestinal tract
 Pertaining to the stomach and intestines. The term 'digestive system' includes the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, anus, pancreas, and liver.... ↪ Read more
Pertaining to the stomach and intestines. The term 'digestive system' includes the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, anus, pancreas, and liver.... ↪ Read more Gastritis
 Inflammation of the stomach. An inflammation of the mucous membrane surrounding the stomach.... ↪ Read more
Inflammation of the stomach. An inflammation of the mucous membrane surrounding the stomach.... ↪ Read more Fungicide
Free radical
 Atom which carries an unpaired electron; free radicals can potentially injure cells and may be responsible for numerous age-related diseases.... ↪ Read more
Atom which carries an unpaired electron; free radicals can potentially injure cells and may be responsible for numerous age-related diseases.... ↪ Read more Foreign body
 Any abnormal substance within the body. Examples include wood slivers, ingested cloth, balls, glass in the feet, etc.... ↪ Read more
Any abnormal substance within the body. Examples include wood slivers, ingested cloth, balls, glass in the feet, etc.... ↪ Read more Flea Dip
 A solution made to kill fleas, applied to an animal and not rinsed off, to allow it to have residual action.... ↪ Read more
A solution made to kill fleas, applied to an animal and not rinsed off, to allow it to have residual action.... ↪ Read more Flatulence
 Increased stomach or intestinal gas. Passing gas from the intestinal tract. May be a sign of disease of the small intestine.... ↪ Read more
Increased stomach or intestinal gas. Passing gas from the intestinal tract. May be a sign of disease of the small intestine.... ↪ Read more First generation
 A description of medications developed from an earlier form of the medication. First generation medications were developed from the original form of the drug; second generation medications are adaptations of first generation drugs; third generation drugs are adaptations of second generation, etc.... ↪ Read more
A description of medications developed from an earlier form of the medication. First generation medications were developed from the original form of the drug; second generation medications are adaptations of first generation drugs; third generation drugs are adaptations of second generation, etc.... ↪ Read more FDA
 Food and Drug Administration. The federal agency which approves drugs and medications for use in animals and people.... ↪ Read more
Food and Drug Administration. The federal agency which approves drugs and medications for use in animals and people.... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Cell-mediated immunity Chelation Chronic Chronic superficial keratitis Chondroprotective nutraceutical Class I, II, III, IV medications Clotting factors CNSPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Animal Hospital and Emergency Center of Las Cruces, 3171 North Main Street, Las Cruces, NM Clovis Veterinary Hospital, 2201 West 7th Street, Clovis, NM Country Club Animal Hospital, 301 West Country Club Road Roswell, NM 88201 USA Del Norte Animal Clinic, 4001 Louisiana Boulevard NE Albuquerque, NM 87110 USA East Lohman Veterinary Clinic, 1700 East Lohman Avenue Las Cruces, NM 88001 USA Great Plains Veterinary Clinic & Hospital, 2720 North Lovington Highway, Hobbs, NM Juan Tabo Animal Clinic, 3804 Juan Tabo Boulevard NE, Albuquerque, NM Abundance of Care Pet Hospital, 267 E Broadway Monticello, NY 12701 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
Doses - OXACILLIN SODIUM OXAZEPAM Doses - OXAZEPAM OXFENDAZOLE Doses - OXFENDAZOLE OXIBENDAZOLE Doses - OXIBENDAZOLE OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDEPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Hamstrung Hand feeding Hand gallop Hand milker Hand strip Handpick Haploid Hard breederveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2025 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online




