 Relieves itching.... ↪ Read more
Relieves itching.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
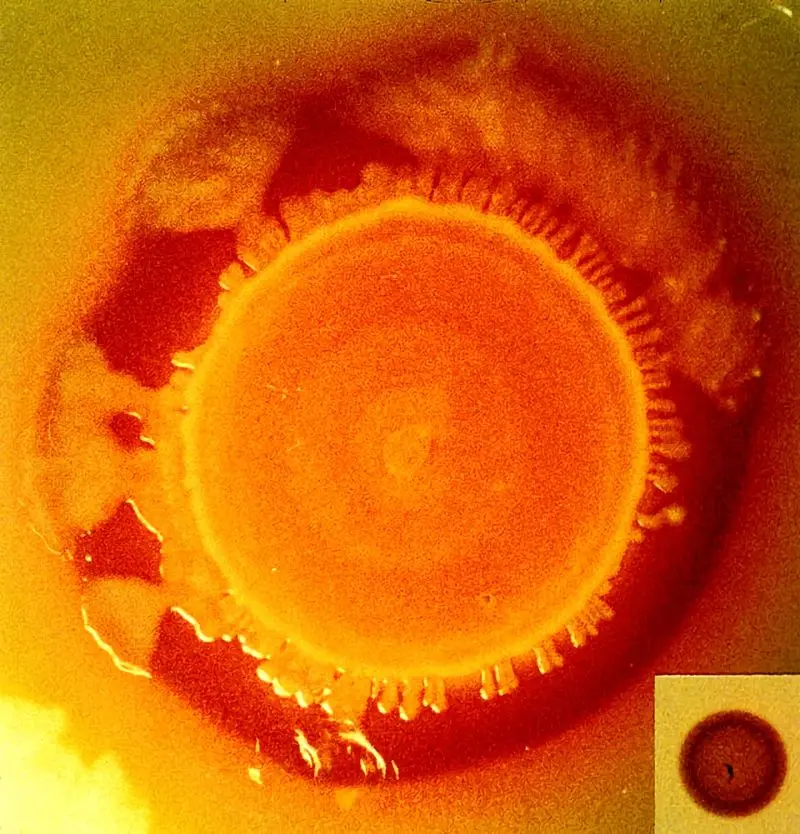 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
Antipruritic
Antiprotozoal
antigen
 A molecular structure on surfaces of such particles as bacteria and viruses. This structure is recognized by the body as 'foreign' and stimulates the body to produce special proteins called antibodies to inactivate this foreign invader. See also antibody.... ↪ Read more
A molecular structure on surfaces of such particles as bacteria and viruses. This structure is recognized by the body as 'foreign' and stimulates the body to produce special proteins called antibodies to inactivate this foreign invader. See also antibody.... ↪ Read more emetic
Anticonvulsant
 A drug used to prevent or decrease the severity of convulsions. Drugs administered to reduce seizures.... ↪ Read more
A drug used to prevent or decrease the severity of convulsions. Drugs administered to reduce seizures.... ↪ Read more Anticoagulation
Anticholinesterase
 a drug that blocks the enzyme acetylcholinesterase; this results in stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system.... ↪ Read more
a drug that blocks the enzyme acetylcholinesterase; this results in stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system.... ↪ Read more Anticholinergic
 Stopping the communications between certain nerves and muscles of the body including those of the gastrointestinal tract and heart. These nerves are called 'parasympathetic' nerves and do such things as constrict the pupils of the eye, stimulate contractions of the muscles in the intestine, and slow... ↪ Read more
Stopping the communications between certain nerves and muscles of the body including those of the gastrointestinal tract and heart. These nerves are called 'parasympathetic' nerves and do such things as constrict the pupils of the eye, stimulate contractions of the muscles in the intestine, and slow... ↪ Read more Antibody Titer
 A measurement of the amount of antibodies in the blood. The test to measure antibodies is usually performed by making a number of dilutions of the blood and then measuring at what dilution there is sufficient antibody to react in the test. For example, a titer of 1:8 (one to eight) means the blood... ↪ Read more
A measurement of the amount of antibodies in the blood. The test to measure antibodies is usually performed by making a number of dilutions of the blood and then measuring at what dilution there is sufficient antibody to react in the test. For example, a titer of 1:8 (one to eight) means the blood... ↪ Read more Antibody
 A protein referred to as immunoglobulin and is derived from lymphocytes originating from the bone marrow (B cells). This form of immunity is essential for extracellular pathogens.
Small disease-fighting proteins produced by certain types of cells called 'B cells'. The proteins are made in response... ↪ Read more
A protein referred to as immunoglobulin and is derived from lymphocytes originating from the bone marrow (B cells). This form of immunity is essential for extracellular pathogens.
Small disease-fighting proteins produced by certain types of cells called 'B cells'. The proteins are made in response... ↪ Read more Anthelmintic
Anorexia
Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Liver Low passage vaccine Lymph Nodes Lymphocytes Lymphokines Macrophage Malabsorption / maldigestion syndrome MalignantPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Falls Road Veterinary Hospital, 10229 Falls Road Potomac, MD 20854 USA Potomac Animal Hospital, 10020 River Rd Potomac, MD 20854 USA Shawsheen Animal Hospital, 1415 Main Street Tewksbury, MA 01876 USA Middlesex County Animal Hospital, 330 Boston Road Billerica, MA 01862 USA Pleasant Valley Animal Hospital, 21 Jackson Street Methuen, MA 01844 USA Watertown Animal Hospital, 404 Main Street Watertown, MA 02472 USA VCA Everett Animal Hospital, 251 Chelsea Street Everett, MA 02149 USA BluePearl - Waltham, 180 Bear Hill Road Waltham, MA 02454 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
TDC 20 CONCENTRATE NoviPet Joint Support for Cats NICH PVPI UREA BOLUS WEST-VET Prepodyne Scrub Universal Post Dip PD 0.5 - 10 DeLaval Opti Blue A.C.T. IODINE MANUFACTURING CONCENTRATE THUJA-ZINC OXIDE OINTMENT Astringent - Antiseptic - Counterirritant Topical OintmentPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Initial problem list Initiation Inotropic Insensible fluid loss Inter-estrus interval Inter-trochanteric fossa Interceptor Interdigital pyodermaveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2025 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online






