 A pathogen that is related to E. coli.... ↪ Read more
A pathogen that is related to E. coli.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
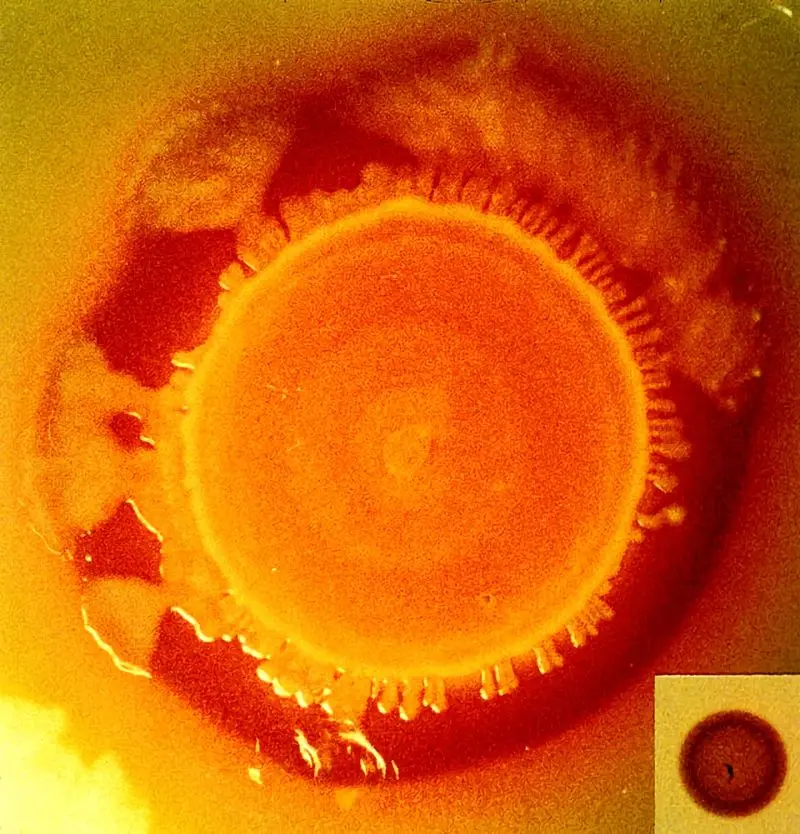 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
Enteric
Enteral
 Delivery of drugs or nutrients to the intestianl tract by deposition in the mouth, stomach or jejunum.... ↪ Read more
Delivery of drugs or nutrients to the intestianl tract by deposition in the mouth, stomach or jejunum.... ↪ Read more Enophthalmos
Energy terminology
 Gross Energy (GE) The total combustible energy in a feed, determined by measuring the amount of heat produced when a feed sample is completely burnt in a bomb calorimeter.... ↪ Read more
Gross Energy (GE) The total combustible energy in a feed, determined by measuring the amount of heat produced when a feed sample is completely burnt in a bomb calorimeter.... ↪ Read more Energy
 A nutrient essential for maintenance, growth, production and reproduction. Energy is required in larger amounts than any other nutrient except water, and is often the limiting factor in livestock production.... ↪ Read more
A nutrient essential for maintenance, growth, production and reproduction. Energy is required in larger amounts than any other nutrient except water, and is often the limiting factor in livestock production.... ↪ Read more Endotoxin
 A substance released from some types of bacteria in the intestine that when absorbed into the blood causes fever and shock called endotoxic shock.... ↪ Read more
A substance released from some types of bacteria in the intestine that when absorbed into the blood causes fever and shock called endotoxic shock.... ↪ Read more Endotoxemia
 A type of shock caused by absorbing endotoxin which is released from some types of bacteria in the intestine when those bacteria die.... ↪ Read more
A type of shock caused by absorbing endotoxin which is released from some types of bacteria in the intestine when those bacteria die.... ↪ Read more Endothelium
Endothelial dystrophy
 An inherited condition seen mainly in older dogs characterized by death of endothelial cells allowing water to enter the stroma resulting in permanent edema.... ↪ Read more
An inherited condition seen mainly in older dogs characterized by death of endothelial cells allowing water to enter the stroma resulting in permanent edema.... ↪ Read more Endoscopy
Endorphin
 A morphine-like peptide that is produced in the brain and which binds to certain receptors to reduce the sensation of pain. 6/18/2003)... ↪ Read more
A morphine-like peptide that is produced in the brain and which binds to certain receptors to reduce the sensation of pain. 6/18/2003)... ↪ Read more Endoparasites
Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Ultrasound / ultrasonography Umbilicus Urate Urinary incontinence Urinary obstruction Urinary retention USP UveitisPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Animal Medical Center of Rome, 13 John Maddox Drive Rome, GA 30165 USA Apalachee Ridge Animal Hospital, 1250 Auburn Road Suite B-207 Dacula, GA 30019 USA Athens Vet Clinic, 2575 Atlanta Highway Athens, GA 30604 USA Baytree Animal Hospital, 2004 Baytree Road, Valdosta, GA BELLS FERRY VETERINARY HOSPITAL, 6410 Hwy 92 ACWORTH, GA 30102 USA VCA Braelinn Village Animal Hospital, 1130 Crosstown Court Peachtree City, GA 30269 USA Briarcliff Animal Clinic, 1850 Johnson Road NE Atlanta, GA 30306 USA VCA Buckhead Animal Hospital, 1911 Piedmont Circle NE Atlanta, GA 30324 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
Durvet Pennox 50 Pennchlor SP 500 Pennchlor S Program 6 Month Injectable for Cats Terramycin® 200 (oxytetracycline) TYPE A MEDICATED ARTICLE Capstar BoviSoft Program SuspensionPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Ethology Etiological Iritis Ischium Isoechoic Isogamy Isolate Isthmusveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2025 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online





