 See: Pyramidal disease.... ↪ Read more
See: Pyramidal disease.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
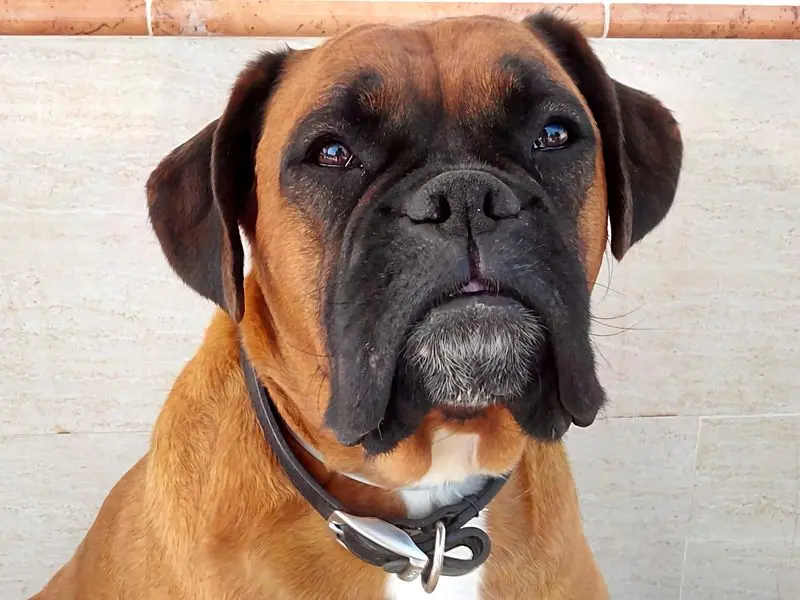 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
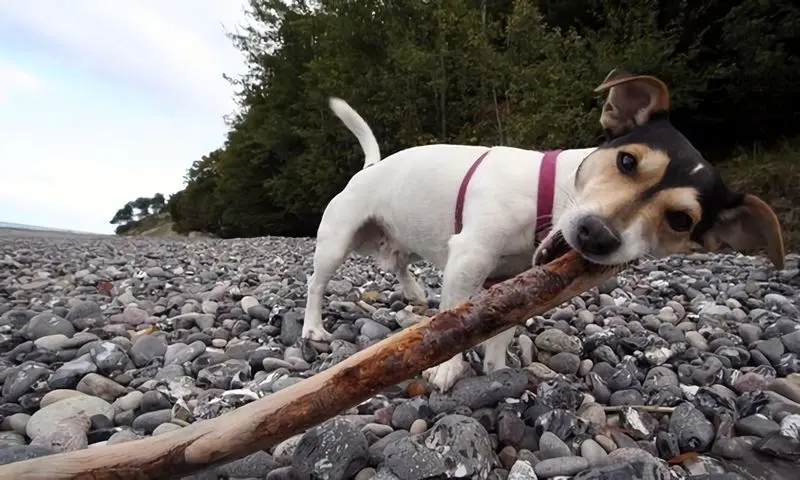 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
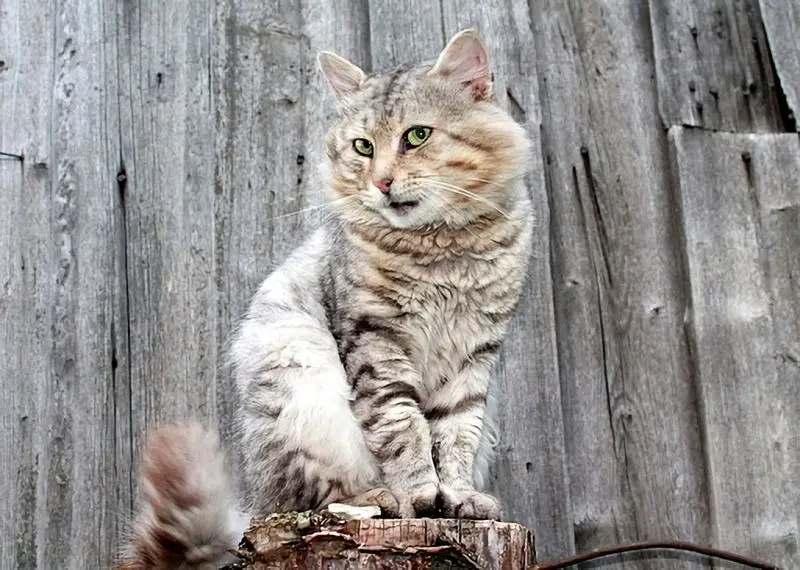 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
EXTENSOR PROCESS DISEASE
EXTENSOR PROCESS
EXTENSION
EXTENDED HEEL
 A long heel on a horseshoe. Usually fit parallel to the center-line of the hoof, and in line with the direction of travel.... ↪ Read more
A long heel on a horseshoe. Usually fit parallel to the center-line of the hoof, and in line with the direction of travel.... ↪ Read more EXPANSION
 (1.)The very sight outward movement of the quarters of the hoof which may occur during weight bearing, and/or the increase in solar width which occurs as the hoof grows down. (2.) In refrence to a horseshoe, expansion describes the practice of fitting the posterior half of the shoe larger than the... ↪ Read more
(1.)The very sight outward movement of the quarters of the hoof which may occur during weight bearing, and/or the increase in solar width which occurs as the hoof grows down. (2.) In refrence to a horseshoe, expansion describes the practice of fitting the posterior half of the shoe larger than the... ↪ Read more EXOSTOSIS
EXFOLIATE
 To shed or flake off dead tissue. The sole of the hoof, for example, normally exfoliates as it grows down.... ↪ Read more
To shed or flake off dead tissue. The sole of the hoof, for example, normally exfoliates as it grows down.... ↪ Read more ETIOLOGY
EPITHELIUM
 Thin membrane tissues covering most of the body's structures and organs, internal and external. Also describes the the first layers that heal over a wound.... ↪ Read more
Thin membrane tissues covering most of the body's structures and organs, internal and external. Also describes the the first layers that heal over a wound.... ↪ Read more EPIPHYSEAL PLATES
 Cartilages near the ends of bones which which allow them to grow lengthwise. As the horse matures, the plates ossify or close. The more distal plates close first. a.k.a: Growth Plates; Epiphyseal Cartilages.... ↪ Read more
Cartilages near the ends of bones which which allow them to grow lengthwise. As the horse matures, the plates ossify or close. The more distal plates close first. a.k.a: Growth Plates; Epiphyseal Cartilages.... ↪ Read more EPIDERMIS
 The outer, protective, nonvascular layer of the skin which covers the dermis. The hoof wall, horny laminae and other horny hoof structures are epidermal.... ↪ Read more
The outer, protective, nonvascular layer of the skin which covers the dermis. The hoof wall, horny laminae and other horny hoof structures are epidermal.... ↪ Read more ELBOW HITTING
 Striking of the point of the elbow joint by the hoof of the same limb or its horseshoe. Injury from elbow hitting is possible, but is sometimes confused with injury caused while the hrse is lying down with his legs folded beneath him.... ↪ Read more
Striking of the point of the elbow joint by the hoof of the same limb or its horseshoe. Injury from elbow hitting is possible, but is sometimes confused with injury caused while the hrse is lying down with his legs folded beneath him.... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Enteral feeding Enteritis Enzymes EPA Epiphora Esophageal reflux Estrogen EstrusPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Iowa State University - Small Animal Hospital, 1809 South Riverside Drive, Ames, IA Jordan Creek Animal Hospital, 3401 Ep True Parkway, West Des Moines, IA Kimberly Crest Veterinary Hospital, 1423 East Kimberly Road Davenport, IA 52807 USA Clinton Parkway Animal Hospital, 4340 Clinton Parkway Lawrence, KS 66047 USA Emporia Veterinary Hospital, 710 Anderson Street Emporia, KS 66801 USA VCA Fairway Animal Hospital, 6000 Mission Road Fairway, KS 66205 USA Wellspring Animal Hospital, 606 North Winterset Lane, Wichita, KS Hill's Pet Nutrition Center, 1035 NE 43rd St Topeka, KS 66617 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
DexaJect NOROCILLIN Injectable Antibiotic ASPIRIN BOLUS Analgesic-Antipyretic ASPIRIN BOLUS - 480 Analgesic-Antipyretic Bactracillin G TM Injectable Antibiotic ASPIRIN BOLUS Analgesic-Antipyretic ASPIRIN BOLUS-480 Analgesic - Antipyretic ASPIRIN BOLUS-240 Analgesic-AntipyreticPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Fluid therapy Fluorescein stain Fluoroscopy Flushing FLUTD Fly strike Follicle Follicle stimulating hormone Abrev FSHveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2026 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online





