 Decrease in the rate or depth of respiration.... ↪ Read more
Decrease in the rate or depth of respiration.... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
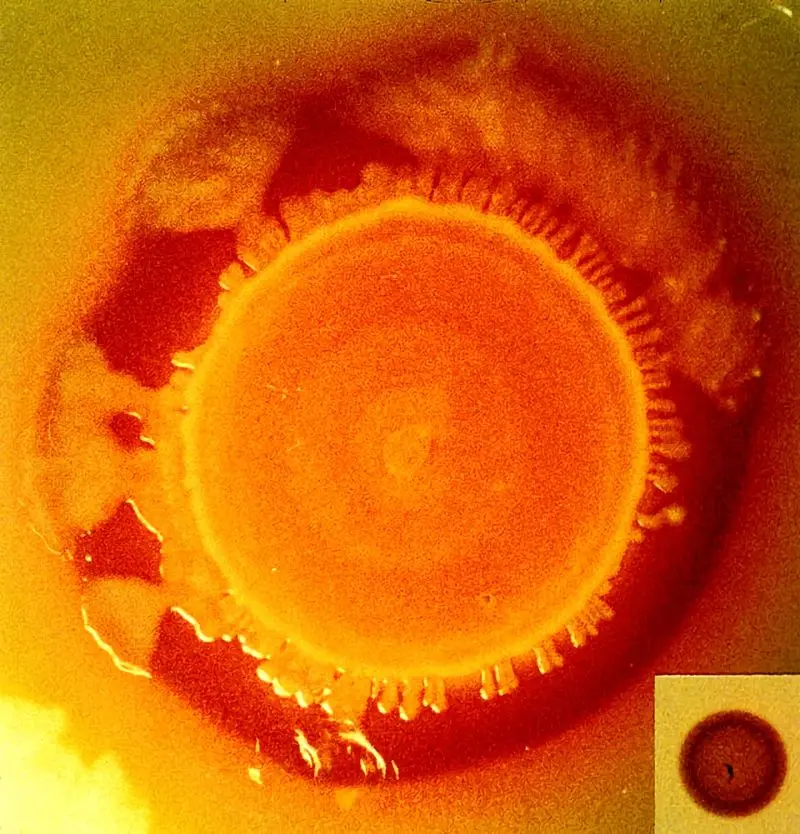 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
Respiratory depression
Resorption
 In pregnancy, a condition in which the fetus dies, and instead of being aborted, the fetal tissue dissolves within the uterus and is absorbed by the mother. The mother will show no outward signs of a fetal resorption.... ↪ Read more
In pregnancy, a condition in which the fetus dies, and instead of being aborted, the fetal tissue dissolves within the uterus and is absorbed by the mother. The mother will show no outward signs of a fetal resorption.... ↪ Read more Resistance
 A term used to describe bacteria which have mutated or changed so they are not affected by an antibiotic that previously killed them or slowed their growth. As more bacteria become resistant to various antibiotics, there are fewer antibiotics which will have an affect on them, thus newer and... ↪ Read more
A term used to describe bacteria which have mutated or changed so they are not affected by an antibiotic that previously killed them or slowed their growth. As more bacteria become resistant to various antibiotics, there are fewer antibiotics which will have an affect on them, thus newer and... ↪ Read more Regulation
 Using insulin to maintain the blood glucose level of an animal within the acceptable range.... ↪ Read more
Using insulin to maintain the blood glucose level of an animal within the acceptable range.... ↪ Read more Reflex ovulator
Recombinant vaccine
 There are certain antigens on viruses and bacteria which are better at stimulating an antibody response by the animal than others. The genes for these antigens can be isolated, and made to produce large quantities of the antigens they code for. A recombinant vaccine contains these antigens, not the... ↪ Read more
There are certain antigens on viruses and bacteria which are better at stimulating an antibody response by the animal than others. The genes for these antigens can be isolated, and made to produce large quantities of the antigens they code for. A recombinant vaccine contains these antigens, not the... ↪ Read more Reagent grade
Rabies
 A fatal virus disease of warm blooded animals including man, that affects the brain and is spread in the saliva of infected animals. Rabid animals have a temperament change. Wild creatures become bold enough to attack human beings, and docile domestic animals may turn on their owners. A viral... ↪ Read more
A fatal virus disease of warm blooded animals including man, that affects the brain and is spread in the saliva of infected animals. Rabid animals have a temperament change. Wild creatures become bold enough to attack human beings, and docile domestic animals may turn on their owners. A viral... ↪ Read more Queening
Queen
 A female cat used for breeding.Unneutered female cat. A female cat. When used as a verb, "to queen" describes a cat giving birth.... ↪ Read more
A female cat used for breeding.Unneutered female cat. A female cat. When used as a verb, "to queen" describes a cat giving birth.... ↪ Read more Pyometra
 An infection of the uterus. Pus accumulation in the uterus, normally caused by bacterial infection, recessive - requires a copy of the gene from both parents to exhibit the trait, Having only one copy of the gene makes the dog a carrier of the trait, and he will never exhibit the trait ? unless the... ↪ Read more
An infection of the uterus. Pus accumulation in the uterus, normally caused by bacterial infection, recessive - requires a copy of the gene from both parents to exhibit the trait, Having only one copy of the gene makes the dog a carrier of the trait, and he will never exhibit the trait ? unless the... ↪ Read more Pyoderma
 An infection of the skin; usually the result of a bacterial invasion. Any purulent (containing or forming pus) skin disease. Skin infection with bacteria. Pyodermas involve coagulase positive bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus intermedius.... ↪ Read more
An infection of the skin; usually the result of a bacterial invasion. Any purulent (containing or forming pus) skin disease. Skin infection with bacteria. Pyodermas involve coagulase positive bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus intermedius.... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Perineal Phagocyte Photoperiod Photosensitivity Phystochemical Phystoestrogen Placebo Plantigrade stancePopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Caputo Animal Hospital, 8188 North Telegraph Dearborn Heights, MI 48127 USA VCA Cedar Animal Hospital, 3604 Cedar Avenue South Minneapolis, MN 55407 USA VCA All About Pets, 5669 Duluth Street Golden Valley, MN 55422 USA Westgate Pet Clinic, 4345 France Avenue South Minneapolis, MN 55410 USA VCA Animal Care Hospital, 1208 East 66th Street Richfield, MN 55423 USA Kansas City Veterinary Care, 7240 Wornall Road Kansas City, MO 64114 USA VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA Platte Woods Animal Hospital, 5901 NW 72nd Street Kansas City, MO 64151 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
Pre Milk Iod 1.0 Pennitracin MD 50 G Denagard 80 Coated Type A Medicated Article SACOX 60 ChlorHex 2X SACOX 60 Neo-Oxy 50/50 panacur® (fenbendazole)Popular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Protein nitrogen units Abrev PNU Protein supplement Prothrombin time Abrev PT Protozoa Proud flesh Pseudohyperparathyroidism Pseudomycetomas Pseudopregnancyveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2025 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online




