 ↪ Doses - CYTARABINE
Chemistry - A synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside antimetabolite, cytarabine occurs as an odorless, white to off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa of 4.35. It is freely soluble in water and slightlysoluble in alcohol. Cytarabine is also commonly known as ARA-C or... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CYTARABINE
Chemistry - A synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside antimetabolite, cytarabine occurs as an odorless, white to off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa of 4.35. It is freely soluble in water and slightlysoluble in alcohol. Cytarabine is also commonly known as ARA-C or... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
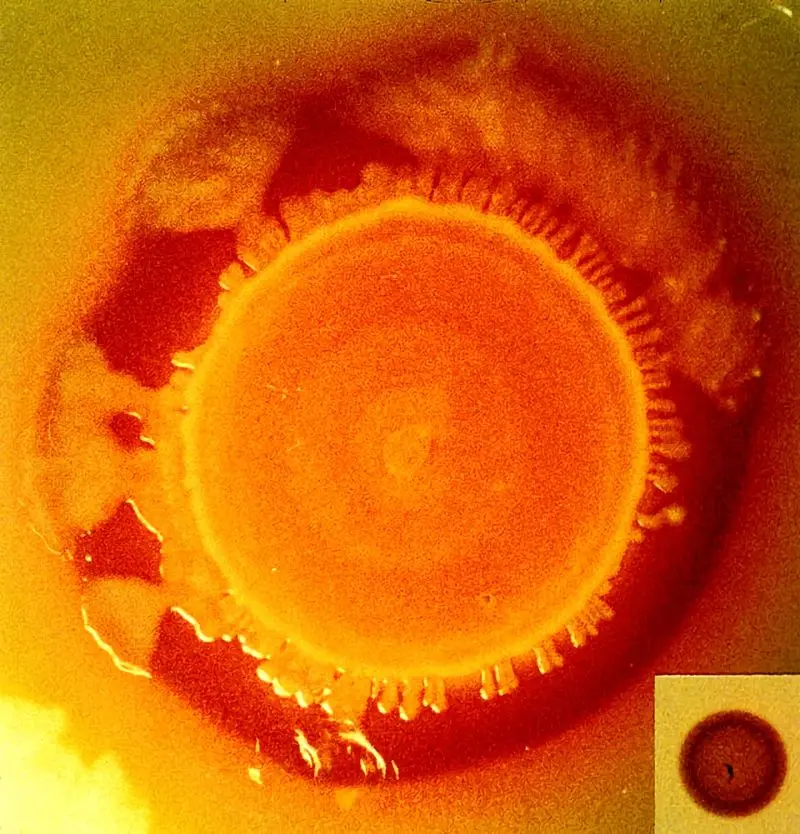 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
CYTARABINE
 ↪ Doses - CYTARABINE
Chemistry - A synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside antimetabolite, cytarabine occurs as an odorless, white to off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa of 4.35. It is freely soluble in water and slightlysoluble in alcohol. Cytarabine is also commonly known as ARA-C or... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CYTARABINE
Chemistry - A synthetic pyrimidine nucleoside antimetabolite, cytarabine occurs as an odorless, white to off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa of 4.35. It is freely soluble in water and slightlysoluble in alcohol. Cytarabine is also commonly known as ARA-C or... ↪ Read more Doses - CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
 ↪ Description - CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
Dogs: As an antihistamine: a) 1.1 mg/kg PO q8-12h (Papich 1992) b) 0.3 - 2 mg/kg PO bid (Bevier 1990)Cats: As an appetite stimulant: a) 2 - 4 mg per cat PO once or twice daily (Davenport 1994) b) 2 mg per cat every 12 hours; may take up to 24 hours for... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
Dogs: As an antihistamine: a) 1.1 mg/kg PO q8-12h (Papich 1992) b) 0.3 - 2 mg/kg PO bid (Bevier 1990)Cats: As an appetite stimulant: a) 2 - 4 mg per cat PO once or twice daily (Davenport 1994) b) 2 mg per cat every 12 hours; may take up to 24 hours for... ↪ Read more CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
 ↪ Doses - CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
Chemistry - An antihistamine that also possesses serotonin antagonist properties, cyproheptadine HCl occurs as a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. Approximately 3.64 mg are soluble inone ml of water and 28.6 mg in one ml of alcohol.Storage, Stability,... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CYPROHEPTADINE HCL
Chemistry - An antihistamine that also possesses serotonin antagonist properties, cyproheptadine HCl occurs as a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. Approximately 3.64 mg are soluble inone ml of water and 28.6 mg in one ml of alcohol.Storage, Stability,... ↪ Read more Doses - CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
 For more information, refer to the protocol references found in the appendix or otherprotocols found in numerous references, including: Handbook of Small Animal Practice (Ogilvie1988), (Cotter 1988), (Stann 1988a); Handbook of Small Animal Therapeutics (Rosenthal 1985); Current Veterinary Therapy... ↪ Read more
For more information, refer to the protocol references found in the appendix or otherprotocols found in numerous references, including: Handbook of Small Animal Practice (Ogilvie1988), (Cotter 1988), (Stann 1988a); Handbook of Small Animal Therapeutics (Rosenthal 1985); Current Veterinary Therapy... ↪ Read more CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
 ↪ Doses - CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
Chemistry - A nitrogen-mustard derivative, cyclophosphamide occurs as a white, crystallinepowder that is soluble in water and alcohol. The commercially available injection has pH of 3 to 7.5. Cyclophosphamide may also be known as CPM, CTX or CYT.Storage,... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
Chemistry - A nitrogen-mustard derivative, cyclophosphamide occurs as a white, crystallinepowder that is soluble in water and alcohol. The commercially available injection has pH of 3 to 7.5. Cyclophosphamide may also be known as CPM, CTX or CYT.Storage,... ↪ Read more Doses - CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
 ↪ Description - CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
Obtain specific information from the laboratory on sample handling and laboratorynormals for cortisol when doing ACTH stimulation tests. ACTH is quite unstable in unfrozenplasma.Dogs: ACTH Stimulation Test: a) Draw baseline blood sample for cortisol... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
Obtain specific information from the laboratory on sample handling and laboratorynormals for cortisol when doing ACTH stimulation tests. ACTH is quite unstable in unfrozenplasma.Dogs: ACTH Stimulation Test: a) Draw baseline blood sample for cortisol... ↪ Read more CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
 ↪ Doses - CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
Chemistry - A 39 amino acid polypeptide, corticotropin is secreted from the anterior pituitary. Thefirst 24 amino acids (from the N-terminal end of the chain) define its biologic activity. Whilehuman, sheep, cattle and swine corticotropin have different... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CORTICOTROPIN (ACTH)
Chemistry - A 39 amino acid polypeptide, corticotropin is secreted from the anterior pituitary. Thefirst 24 amino acids (from the N-terminal end of the chain) define its biologic activity. Whilehuman, sheep, cattle and swine corticotropin have different... ↪ Read more Doses - COLCHICINE
 Colchicine may have some efficacy in the treatment of amyloidosis, but veterinary dosages areapparently unavailable at this time.Dogs: For the adjunctive treatment of hepatic cirrhosis/fibrosis: a) 0.025 - 0.03 mg/kg/day PO. Benefit is unproven. (Johnson and Sherding 1994) b) 0.025 mg/kg PO per... ↪ Read more
Colchicine may have some efficacy in the treatment of amyloidosis, but veterinary dosages areapparently unavailable at this time.Dogs: For the adjunctive treatment of hepatic cirrhosis/fibrosis: a) 0.025 - 0.03 mg/kg/day PO. Benefit is unproven. (Johnson and Sherding 1994) b) 0.025 mg/kg PO per... ↪ Read more COLCHICINE
 ↪ Doses - COLCHICINE
Chemistry - An antigout drug possessing many other pharmacologic effects, colchicine occurs asa pale yellow, amorphous powder or scales. It is soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol.Storage, Stability, Compatibility Colchicine tablets should be stored in tight,... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - COLCHICINE
Chemistry - An antigout drug possessing many other pharmacologic effects, colchicine occurs asa pale yellow, amorphous powder or scales. It is soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol.Storage, Stability, Compatibility Colchicine tablets should be stored in tight,... ↪ Read more Doses - CODEINE PHOSPHATE
 ↪ Description - CODEINE PHOSPHATE
Dogs: As an antitussive: a) 0.1 - 0.3 mg/kg PO q6-8h (Papich 1992) b) 1 - 2 mg/kg PO q6-12h (Fenner 1994) As an analgesic: a) 0.5 - 1 mg/kg PO q6-8h (Papich 1992) b) In combination with acetaminophen: Using a 60 mg codeine and 300 mg... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - CODEINE PHOSPHATE
Dogs: As an antitussive: a) 0.1 - 0.3 mg/kg PO q6-8h (Papich 1992) b) 1 - 2 mg/kg PO q6-12h (Fenner 1994) As an analgesic: a) 0.5 - 1 mg/kg PO q6-8h (Papich 1992) b) In combination with acetaminophen: Using a 60 mg codeine and 300 mg... ↪ Read more CODEINE PHOSPHATE
 ↪ Doses - CODEINE PHOSPHATE
Chemistry - A phenanthrene-derivative opiate agonist, codeine is available as the base and threeseparate salts. Codeine base is slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Codeinephosphate occurs as fine, white, needle-like crystals or white,... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - CODEINE PHOSPHATE
Chemistry - A phenanthrene-derivative opiate agonist, codeine is available as the base and threeseparate salts. Codeine base is slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Codeinephosphate occurs as fine, white, needle-like crystals or white,... ↪ Read more Doses - CLOXACILLIN SODIUM, CLOXACILLIN BENZATHINE
 ↪ Description - CLOXACILLIN SODIUM, CLOXACILLIN BENZATHINE
Author's (Plumb) note: Injectable form is not available in the U.S.A.Dogs: For susceptible infections: a) 20 - 40 mg/kg PO q8h (Vaden and Papich 1995) b) 10 - 15 mg/kg q6h PO, IV, or IM (Greene 1984) c) For Staph. diskospondylitis... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - CLOXACILLIN SODIUM, CLOXACILLIN BENZATHINE
Author's (Plumb) note: Injectable form is not available in the U.S.A.Dogs: For susceptible infections: a) 20 - 40 mg/kg PO q8h (Vaden and Papich 1995) b) 10 - 15 mg/kg q6h PO, IV, or IM (Greene 1984) c) For Staph. diskospondylitis... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Metastatis Methemoglobinemia Microfilaria Microfilaricide Microorganism Mineralocorticoids Miticide MitochondriaPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Germantown Parkway Animal Hospital, 886 Cordova Station Avenue, TN Southwind Animal Hospital, 7910 Winchester Rd Memphis, TN 38125 USA The County Seat Animal Hospital, 145 West Center Street Hernando, MS 38632 USA Manchester's Animal Medical Center LLC, 1634 220th St Manchester, IA 52057 USA Town & Country Veterinary Clinic, 1506 E 5th Street Tama, IA 52339 USA Riverside Animal Hospital, P.C., 938 Grandview Avenue Muscatine, IA 52761 USA Riverside Veterinary Care, 159 River Street Rutland, VT 05701 USA Riverside Pet Care At Ludlow, 185 Main St Ludlow, VT 05149 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
Doses - ENALAPRIL MALEATE, ENALAPRILAT ENROFLOXACIN Doses - ENROFLOXACIN EPHEDRINE SULFATE Doses - EPHEDRINE SULFATE EPINEPHRINE Doses - EPINEPHRINE EPOETIN ALFA, EPOETIN BETA, ERYTHROPOIETIN, EPO, r-HUEPOPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
SEALANT SEATING OUT SEEDY TOE SELENIUM SEMILUNAR CREST SENSITIVE FROG SENSITIVE LAMINAE SENSITIVE SOLEveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2026 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online

