 ↪ Doses - VASOPRESSIN
Note: Vasopressin tannate is no longer commercially available in the USA. Chemistry - A hypothalamic hormone stored in the posterior pituitary, vasopressin is a 9-aminoacid polypeptide with a disulfide bond. In most mammals (including dogs and humans), the... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - VASOPRESSIN
Note: Vasopressin tannate is no longer commercially available in the USA. Chemistry - A hypothalamic hormone stored in the posterior pituitary, vasopressin is a 9-aminoacid polypeptide with a disulfide bond. In most mammals (including dogs and humans), the... ↪ Read more Veterinary Drug Handbook (VDH) is the reference veterinarians turn to when they want an independent source of information on the drugs that are used in veterinary medicine today.
-
 Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans?
Is veterinary Liniment Gel safe for humans? -
 Giving Your Cat A Pill
Giving Your Cat A Pill -
 Dog Aggression
Dog Aggression -
 Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health
Dogs May Help Boost Infant Health -
 Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis
Animal-Assisted Therapy, Veterinary Social Work, & Social Work With People & Pets in Crisis -
 On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets
On-demand veterinary service gives advice on poorly pets -
 Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs?
Should we stop throwing sticks for dogs? -
 What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine?
What does PU/PD mean in veterinary medicine? -
 Can breathing in cat hair be harmful?
Can breathing in cat hair be harmful? -
 Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores
Bill calls for ban on sales of dogs, cats in Maine pet stores -
 What does DVM stand for in veterinary?
What does DVM stand for in veterinary? -
 Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior
Common Meanings Of Cat Behavior -
 Curing Bad Cat Breath
Curing Bad Cat Breath -
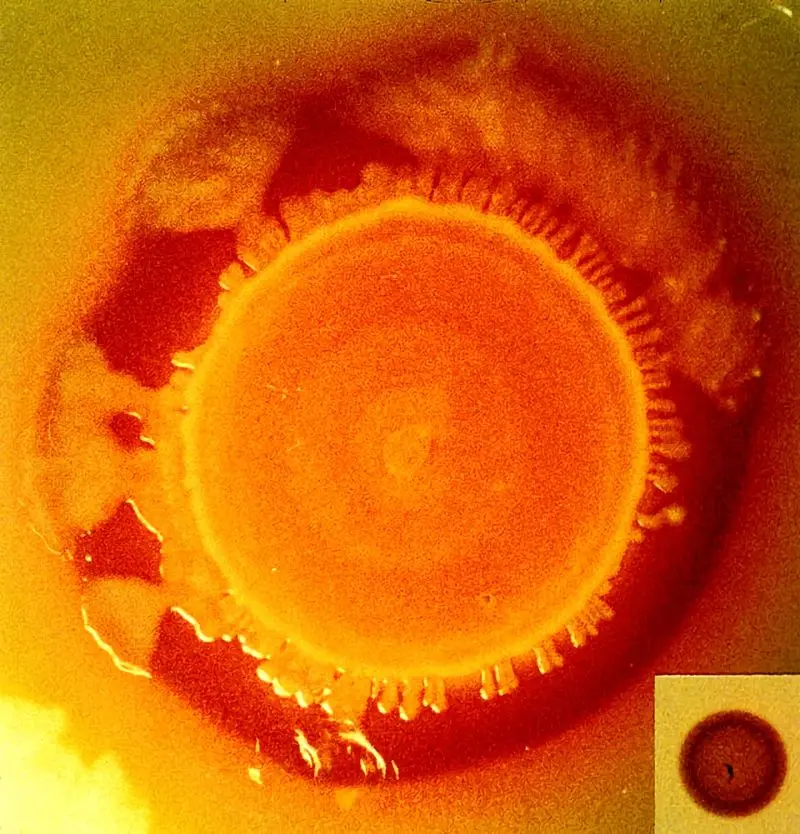 New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators
New Tracking Tool for Pathogen Investigators -
Can binturongs be kept as pets?
-
 How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
How long do instruments stay sterile after autoclaving veterinary?
VASOPRESSIN
 ↪ Doses - VASOPRESSIN
Note: Vasopressin tannate is no longer commercially available in the USA. Chemistry - A hypothalamic hormone stored in the posterior pituitary, vasopressin is a 9-aminoacid polypeptide with a disulfide bond. In most mammals (including dogs and humans), the... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - VASOPRESSIN
Note: Vasopressin tannate is no longer commercially available in the USA. Chemistry - A hypothalamic hormone stored in the posterior pituitary, vasopressin is a 9-aminoacid polypeptide with a disulfide bond. In most mammals (including dogs and humans), the... ↪ Read more Doses - VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
 ↪ Description - VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Dogs: a) 75 - 200 mg/kg PO tid (Bunch 1986) b) 30 - 180 mg/kg/day PO divided tid (Schunk 1988) c) 170 - 185 mg/kg/day divided bid-tid (Kay and Aucoin 1985) Monitoring Parameters - 1) Anticonvulsant efficacy 2) If used... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Dogs: a) 75 - 200 mg/kg PO tid (Bunch 1986) b) 30 - 180 mg/kg/day PO divided tid (Schunk 1988) c) 170 - 185 mg/kg/day divided bid-tid (Kay and Aucoin 1985) Monitoring Parameters - 1) Anticonvulsant efficacy 2) If used... ↪ Read more VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
 ↪ Doses - VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Chemistry - Structurally unrelated to other anticonvulsant agents, valproic acid, valproate sodium, divalproex sodium are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Valproic acid occurs as a colorless to paleyellow clear liquid. It is... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - VALPROIC ACID, VALPROATE SODIUM, DIVALPROEX SODIUM
Chemistry - Structurally unrelated to other anticonvulsant agents, valproic acid, valproate sodium, divalproex sodium are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Valproic acid occurs as a colorless to paleyellow clear liquid. It is... ↪ Read more Doses - URSODIOL
 Dogs: For adjunctive treatment of chronic hepatitis: a) 5 - 15 mg/kg PO divided q12h, with immunosuppressive therapy. (Note: Use of this drug at thisdose is preliminary, but promising) (Johnson and Sherding 1994) b) 10 - 15 mg/kg PO once daily (Leveille-Webster and Center 1995)Cats: For... ↪ Read more
Dogs: For adjunctive treatment of chronic hepatitis: a) 5 - 15 mg/kg PO divided q12h, with immunosuppressive therapy. (Note: Use of this drug at thisdose is preliminary, but promising) (Johnson and Sherding 1994) b) 10 - 15 mg/kg PO once daily (Leveille-Webster and Center 1995)Cats: For... ↪ Read more URSODIOL
 ↪ Doses - URSODIOL
Chemistry A naturally occurring bile acid, ursodiol, also known as ursodeoxycholic acid has a molecular weight of 392.6.Storage, Stability, Compatibility Unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer, ursodiol capsules should be stored at room temperature (15-30°C)... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - URSODIOL
Chemistry A naturally occurring bile acid, ursodiol, also known as ursodeoxycholic acid has a molecular weight of 392.6.Storage, Stability, Compatibility Unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer, ursodiol capsules should be stored at room temperature (15-30°C)... ↪ Read more Doses - TYLOSIN
 Dogs: For susceptible infections: a) 6.6 - 11 mg/kg IM q12-24h (Ford and Aronson 1985) b) For chronic colitis: Tylan® Plus Vitamins: 40 - 80 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses;either mixed with food (tastes bitter) or as a bolus mixed with water. Use at recommended dose for 2 weeks and then... ↪ Read more
Dogs: For susceptible infections: a) 6.6 - 11 mg/kg IM q12-24h (Ford and Aronson 1985) b) For chronic colitis: Tylan® Plus Vitamins: 40 - 80 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses;either mixed with food (tastes bitter) or as a bolus mixed with water. Use at recommended dose for 2 weeks and then... ↪ Read more TYLOSIN
 ↪ Doses - TYLOSIN
Chemistry - A macrolide antibiotic related structurally to erythromycin, tylosin is produced from Streptomyces fradiae. It occurs as an almost white to buff-colored powder with a pKa of 7.1. It isslightly soluble in water and soluble in alcohol. Tylosin is considered to be... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - TYLOSIN
Chemistry - A macrolide antibiotic related structurally to erythromycin, tylosin is produced from Streptomyces fradiae. It occurs as an almost white to buff-colored powder with a pKa of 7.1. It isslightly soluble in water and soluble in alcohol. Tylosin is considered to be... ↪ Read more Doses - TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
 ↪ Description - TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
It is recommended to warm the solution to near body temperature before injecting; give IMinjections into large muscle areas.Dogs: a) 1.1 mg/kg IM q6-12h prn (Package Insert; Re-Covr® - Solvay) b) 1 mg/kg PO q12h; 1 mg/kg IM (Kirk 1986)Cats: a) 1.1... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
It is recommended to warm the solution to near body temperature before injecting; give IMinjections into large muscle areas.Dogs: a) 1.1 mg/kg IM q6-12h prn (Package Insert; Re-Covr® - Solvay) b) 1 mg/kg PO q12h; 1 mg/kg IM (Kirk 1986)Cats: a) 1.1... ↪ Read more TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
 ↪ Doses - TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
Chemistry - An ethylenediamine-derivative antihistamine, tripelennamine HCl occurs as a white, crystalline powder which will slowly darken upon exposure to light. It has a melting range of 188-192°C and pKas of 3.9 and 9.0. One gram is soluble in 1 ml of... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - TRIPELENNAMINE HCL
Chemistry - An ethylenediamine-derivative antihistamine, tripelennamine HCl occurs as a white, crystalline powder which will slowly darken upon exposure to light. It has a melting range of 188-192°C and pKas of 3.9 and 9.0. One gram is soluble in 1 ml of... ↪ Read more Doses - TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
 ↪ Description - TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
Trimeprazine: a)In general, for all species, all routes: 1.1 - 4.4 mg/kg qid (Swinyard 1975)Dogs: a) 2.5 mg/10 lbs up to 40 pounds; for patients over 40 lb.: 15 mg bid, after 4 days, reduce the dose to 1/2 of... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
Trimeprazine: a)In general, for all species, all routes: 1.1 - 4.4 mg/kg qid (Swinyard 1975)Dogs: a) 2.5 mg/10 lbs up to 40 pounds; for patients over 40 lb.: 15 mg bid, after 4 days, reduce the dose to 1/2 of... ↪ Read more TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
 ↪ Doses - TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
Chemistry - A phenothiazine antihistamine related to promethazine, trimeprazine tartrate occurs asan odorless, white, to off-white crystalline powder with a melting range of 160-164°C. Approximately 0.5 gm is... ↪ Read more
↪ Doses - TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE, TRIMEPRAZINE TARTRATE WITH PREDNISOLONE
Chemistry - A phenothiazine antihistamine related to promethazine, trimeprazine tartrate occurs asan odorless, white, to off-white crystalline powder with a melting range of 160-164°C. Approximately 0.5 gm is... ↪ Read more Doses - TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
 ↪ Description - TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
Dogs: For glucocorticoid effects: a) 0.25 - 2 mg PO once daily for 7 days; 0.11 - 0.22 mg/kg IM or SQ. (Kirk 1989) b) 0.11 - 0.22 mg/kg PO, IM or SQ once daily. (Jenkins 1985) c) For tablets: 0.11 mg/kg PO initially once a day, may increase to 0.22... ↪ Read more
↪ Description - TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
Dogs: For glucocorticoid effects: a) 0.25 - 2 mg PO once daily for 7 days; 0.11 - 0.22 mg/kg IM or SQ. (Kirk 1989) b) 0.11 - 0.22 mg/kg PO, IM or SQ once daily. (Jenkins 1985) c) For tablets: 0.11 mg/kg PO initially once a day, may increase to 0.22... ↪ Read more Popular Diagnoses
Packed cell volume (PCV, hematocrit) Reflex ovulator Mucolytic Microfilaricide Bronchodilator Hematocrit Glucocorticoid Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ↪ All veterinary diagnoseOther Diagnoses
Placebo Plantigrade stance Plaque Platelets Polyarthritis Polydactyl Polydipsia PolyestrousPopular Veterinary Clinics
VCA Welborn Animal Hospital, 7860 Washington Avenue Kansas City, KS 66112 USA MedVet Columbus, 300 East Wilson Bridge Road, Worthington, OH Rutland Veterinary Clinic & Surgical Center, 90 East Pittsford Road, Rutland, VT VCA Paradise Valley Emergency Animal Hospital, 6969 East Shea Boulevard Suite 150 Scottsdale, AZ 85254 USA Connecticut Veterinary Center & Pet ER, 470 Oakwood Ave West Hartford, CT 06110 USA Norway Veterinary Hospital, 10 Main St P.O. Box 273 Norway, ME 04268 USA Craig Road Animal Hospital, 5051 West Craig Road, Las Vegas, NV Abri Veterinary Hospital Inc, 1449 Trademart Boulevard Winston-Salem, NC 27127 USA ↪ All veterinary clinicsOther Veterinary Clinics
Aurora Veterinary Hospital, 8821 Aurora Avenue North Seattle, WA 98103 USA Belfair Animal Hospital, 23240 NE State, Belfair, WA Best Friend's Veterinary Center, 33285 State Route 20 Oak Harbor, WA 98277 USA Brady Veterinary Hospital, 450 Monte-Brady Road Montesano, WA 98563 USA Animal Care Associates, 840 Oakwood Road Charleston, WV 25314 USA Audubon Animal Clinic, 17 Chenoweth Drive Bridgeport, WV 26330 USA Greenbrier Veterinary Hospital, 275 Plane View Drive, Lewisburg, WV Ayers Animal Hospital Inc, 1514 Norway Avenue Huntington, WV 25705 USAPopular Drugs
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE Doses - PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM Doses - METHYLPREDNISOLONE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE ACETATE, METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE ACEPROMAZINE MALEATE Doses - PREDNISOLONE, PREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE, PREDNISOLONE ACETATE, PREDNISONE Doses - FURAZOLIDONE Doses - FERROUS SULFATE Doses - LEVAMISOLE ↪ All veterinary drugOther Drugs
Program 6 Month Injectable for Cats Terramycin® 200 (oxytetracycline) TYPE A MEDICATED ARTICLE Capstar BoviSoft Program Suspension ASPIRIN BOLUS ASPIRIN 240 GRAIN BOLUSES ANALGESIC BOVI-KOTEPopular Terms
Subalbinotic Steatis Uteroverdin Paradoxical CSF acidosis Figure of 8 suture pattern Nerve root signature Ovariohysterectomy Abrev OVH Signalment ↪ All veterinary termOther Terms
Tethering Tetraplegia Encephalomyelitis Enclosure Encrustation Encyst Endectocide Endemicveterinary-help.com
© 2011-2026 Veterinary Clinics, Diagnoses, Terms and Drug Handbook Online

